See the Pen Two-Sum by Dhiviya Dhanasekar (@dhiviyadhanasekar) on CodePen.
Monday, March 29, 2021
Two Sum
Box Stacking - Dynamic Programming
See the Pen Box Stacking Problem - Dynamic Programming by Dhiviya Dhanasekar (@dhiviyadhanasekar) on CodePen.
Thursday, March 25, 2021
What happens when you enter a URL in the browser? - UI Edition
- browser checks cache; if requested object is in cache and is fresh, skip to #9
- browser asks OS for server's IP address
- OS makes a DNS lookup and replies the IP address to the browser. Each DNS can forward to other DNS if it doesn’t have the data, till it reaches the root DNS (which will have the ip address)
- browser opens a TCP connection to server (this step is much more complex with HTTPS) at port 80.
- In case of HTTPs, it also creates a SSL connection (refer to stamp’s book)
- browser sends the HTTP request through TCP connection
- browser receives HTTP response and may close the TCP connection, or reuse it for another request
- browser checks if the response is a redirect or a conditional response (3xx result status codes), authorization request (401), error (4xx and 5xx), etc.; these are handled differently from normal responses (2xx)
- if cacheable, response is stored in cache
- browser decodes response (e.g. if it's gzipped)
- browser determines what to do with response (e.g. is it a HTML page, is it an image, is it a sound clip?)
- browser renders response, or offers a download dialog for unrecognized types
Sunday, March 21, 2021
Length of the longest substring
See the Pen Length of the longest substring by Dhiviya Dhanasekar (@dhiviyadhanasekar) on CodePen.
Saturday, March 20, 2021
React lifecycle methods and the order in which they are called
See the Pen React lifecycle methods & their ordering by Dhiviya Dhanasekar (@dhiviyadhanasekar) on CodePen.
Friday, March 19, 2021
String to Leet
See the Pen
String to Leet by Dhiviya Dhanasekar (@dhiviyadhanasekar)
on CodePen.
Lessons Learnt:
mapper = {'a': 0};
if(mapper['a']) ---> is false
0 || undefined ---> is undefined
undefined || 0 ---> is 0
Friday, March 12, 2021
Create a line on a graph given 2 coordinates that define the line
See the Pen Graph Line Plot by Dhiviya Dhanasekar (@dhiviyadhanasekar) on CodePen.
Saturday, March 6, 2021
CSS Box Sizing
box-sizing: 'content-box' => width = width(content), does not include padding, border or margins -> default behaviour
box-sinzing: 'border-box' => width = width(content) + padding + border, does not include margins
Wednesday, March 3, 2021
Binary Heap properties
A Binary Heap is a Binary Tree with following properties.
1) It’s a complete tree (All levels are completely filled except possibly the last level and the last level has all keys as left as possible). This property of Binary Heap makes them suitable to be stored in an array.
2) A Binary Heap is either Min Heap or Max Heap. In a Min Binary Heap, the key at root must be minimum among all keys present in Binary Heap. The same property must be recursively true for all nodes in Binary Tree. Max Binary Heap is similar to MinHeap.
Arr[(i-1)/2] Returns the parent node Arr[(2*i)+1] Returns the left child node Arr[(2*i)+2] Returns the right child node
Arr[(n/2) .... (n-1)] => will contain the leaf nodes, if n is the length of the array or total number of nodes.
The traversal method use to achieve Array representation is Level Order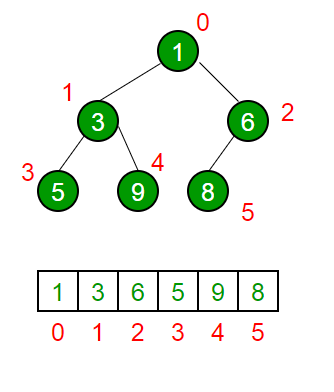
Source: geeks for geeks
Tuesday, March 2, 2021
Powers of 2 to remember for scalability questions
Binary Tree - DFS Preorder (Stacks)
See the Pen Binary Tree - DFS Preorder (Stacks) by Dhiviya Dhanasekar (@dhiviyadhanasekar) on CodePen.
Binary Tree - DFS PostOrder (Recursion)
See the Pen DFS - Binary Tree PostOrder (Recursion) by Dhiviya Dhanasekar (@dhiviyadhanasekar) on CodePen.
Monday, March 1, 2021
Binary Tree - DFS PreOrder (Recursive)
See the Pen Binary Tree DFS Pre-order traversal by Dhiviya Dhanasekar (@dhiviyadhanasekar) on CodePen.
Binary Tree - DFS Inorder Traversal (Recursion)
See the Pen DFS - Binary Tree Inorder (Recursion) by Dhiviya Dhanasekar (@dhiviyadhanasekar) on CodePen.

